Square
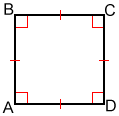
A square is a quadrilateral with four right angles and four congruent sides, as shown in the figure below. A square is a regular quadrilateral.

In algebra, the square of a number is the number multiplied by itself. For example, the square of n is written as "n2" and is equal to n × n.
Sides of a square
The sides of a square are congruent. Also, the opposite sides of a square are parallel, and the adjacent sides are perpendicular to each other.
In the square below, AB//CD and AD//BC. Also, AD and BC are perpendicular to AB and CD respectively.
Angles of a square
The angles of a square are all congruent and equal to 90°. Accordingly, the external angles of a square are also right angles. In the diagram above, the angles marked with a red square are all right triangles.
Diagonals of a square
A square has two congruent diagonals. The diagonals of a square have special properties:
- The two diagonals and in the figure below of a square are perpendicular bisectors of each other. The point of intersection of the diagonals is the center of the square (E in the figure below).

- The diagonals of a square bisect its angles, forming 8 congruent angles, each measuring 45°, forming two pairs of four congruent 45°-45°-90° triangles: △ABC, △ADC, △BAD, and △BCD; △ABE, △ADE, △BCE, and △CDE.

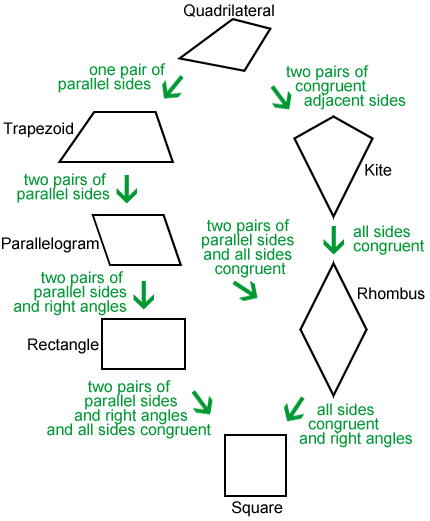
Special quadrilaterals
A square is a regular quadrilateral. It is also a special case of a parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, trapezoid, and kite:
Symmetry in a square
As a regular quadrilateral, a square has 4 lines of symmetry and a rotational symmetry of order 4, which means that it can be rotated in such a way that it will look the same as the original shape 4 times in 360°.
| Line of symmetry | Rotational symmetry |
|---|---|
 |
 |
| 4 lines of symmetry | Four 90° angles of rotation |
Area and perimeter of a square
Given that a square has four right angles and four congruent sides, the area and perimeter of a square are:
area = a2
perimeter = 4a
where a is the length of the side.
